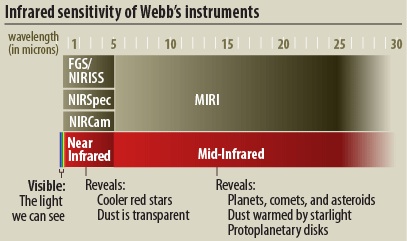
NIRCam detects light from: the earliest stars and galaxies in the process of formation, the population of stars in nearby galaxies, as well as young stars in the Milky Way and Kuiper Belt objects.
NIRCam

Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam)
The Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) is Webb's primary imager that covers the infrared wavelength range 0.6 to 5 microns. NIRCam detects light from: the earliest stars and galaxies in the process of formation, the population of stars in nearby galaxies, as well as young stars in the Milky Way and Kuiper Belt objects. NIRCam is equipped with coronagraphs, instruments that allow astronomers to take pictures of very faint objects around a central bright object, like stellar systems. NIRCam's coronagraphs work by blocking a brighter object's light, making it possible to view the dimmer object nearby - just like shielding the sun from your eyes with an upraised hand can allow you to focus on the view in front of you. With the coronagraphs, astronomers hope to determine the characteristics of planets orbiting nearby stars.
Video: Nircam 3d Diagram Rotation
NIRCam was built by the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin.
IN DEPTH: Technical Details for NIRCam
The NIRCam has ten mercury-cadmium-telluride (HgCdTe) detector arrays. These are analogous to CCDs found in ordinary digital cameras. The NIRCam is a science instrument but also an Optical Telescope Element wavefront sensor, which provides something similar to instant LASIK vision correction.
Other Resources
- Space Telescope Science Institute has a technical page on NIRCam
- Archive of NIRCam images
- Our page about the detectors in our instruments